Diamond
Diamond is the well known hardest material in nature, formed by carbon atoms. Diamond is a kind of rare material naturally formed deeply down the earth, with high temperature and pressure.
Diamond is being labeled as the icon of forever love and wedding back to the very past in human history.
Standards
How can we choose a diamond? The price of a diamond depends on the weight, color, brightness, clarity, transparency, cutting and symmetry.
The well known standard of diamond is “4Cs”, ie. Carat, Color, Clarity and Cut.
Carat
Carat, is the basic unit of the weight of a diamond. 1Carat = 0.2 gram, ie. 100 points.
Basically, more the weight more the cost or each carat it is.。
Clarity
Clarity is defined by the amount of flaws. It might be natural impurities or cracks. The number, location, and size of the defects will affect the grading. Only 20% of the diamond mines can be a gem, and the rest can usually only be used for industrial purposes because of the massive amount of flaws. The diamond with “Flawless” level is very rare, known as the “Museum Grade” diamonds. Using 10 times magnifying glass can inspect the type and amount of flaws.
The grading is defined as follows:
- FL - Flawless
- Flawless under 10 times magnifying glass.
- IF - Internally flawless
- Minor scratches on surface under 10 times magnifying glass.
- VVS1, VVS2 - Very, Very Slightly Included
- Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
- VS1 and VS2 - Very Slightly Included
- Inclusions are clearly visible under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor
- SI1 and SI2 - Slightly Included
- Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification
- I1, I2 and I3 - Included
- Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance
Color
The color of the diamond is reflecting the chemical impurities. Completely pure diamonds are transparent and colorless. Different colors of a diamond will affect its value. Most of diamonds are yellow because of the nitrogen atoms. Stronger the yellowish color of diamond, the lower the value it is. However, pink or blue diamond prices are higher. The prices of strong pink or blue color diamonds are extremely high.
The color grades of diamonds are defined according to the degree of yellowish color, from grade D to Z.

Cut
Precise artistry and workmanship are required to fashion a stone by cutting it. Cut is crucial to the appearance and value of the diamond. It is also the most complicated and difficult to analyze of all the 4Cs.
Cut affects the Visual Effects such as:
| Brightness: |
Internal and external white light reflected from a diamond |
| Fire: |
The scattering of white light into all the colors of the rainbow |
| Scintillation: |
The amount of sparkle a diamond produces, and the pattern of light and dark areas caused by reflections within the diamond.
Grades of cut include: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, Poor |
Shape
Diamond Shape and Cut

Circle |

Oval |
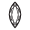
Marquise Brilliant |

Pear |
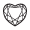
Heart |

Emerald |
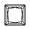
Princess |
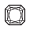
Radiant |
International Gem Identification
-
Gemological Institute Of America (GIA)
-
International Gemological Institute
-
European Gemological Laboratory
-
比利時鑽石高等評議會 (HRD)

-
American Gem Society (AGS)
